
Scores for Stratification
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
MISSION
To enable the accurate evaluation of SLE disease activity by stratifying study participants into “active” or “inactive” disease cohorts using SLEDAI scores.
CHALLENGES
Collect biospecimens at least five times weekly while gathering all necessary clinical and laboratory data within 10 days of collection to calculate SLEDAI scores.
SOLUTION
We quickly recruited and enrolled SLE patients to participate—generating accurate SLEDAI scores within the defined study timelines. Repeatedly measured data obtained through longitudinal sampling and clinical evaluations coupled with their frequent transfer to the sponsor’s clinical study team ensured successful study execution.
Applying the SLE Disease Activity Index to Research Study Designs
The broad spectrum of clinical manifestations seen in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) makes it challenging to characterize the disease meaningfully. Particularly problematic for researchers and physicians alike is the apparent classification of differences between acute episodes and chronic disease damage.
To that end, the SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI-2K) functions to standardize the assessment of disease severity by clinicians globally. This tool consists of 24 weighted variables (eight laboratory and 16 clinical) of nine organ systems for disease activity¹. Clinical assessments are necessary within 10 days of laboratory test results for the most accurate score calculation. Stratification of patients based on SLEDAI score can be applied to participant cohort inclusion and exclusion criteria for an added level of study design rigor when assessing intervention effectiveness at different disease stages.
Study Requirements
Participants
Commitment
Biospecimens
Downstream Analyses
40 SLE patients with “active” disease and 60 with “inactive” disease
Five samples collected per week
Whole blood, often requiring delivery within 2 hours post-collection to preserve sample integrity
Clinical symptom report within 10 days of sample collection paired with laboratory
results to calculate the SLEDAI score
How Did We Rise to the Challenge?
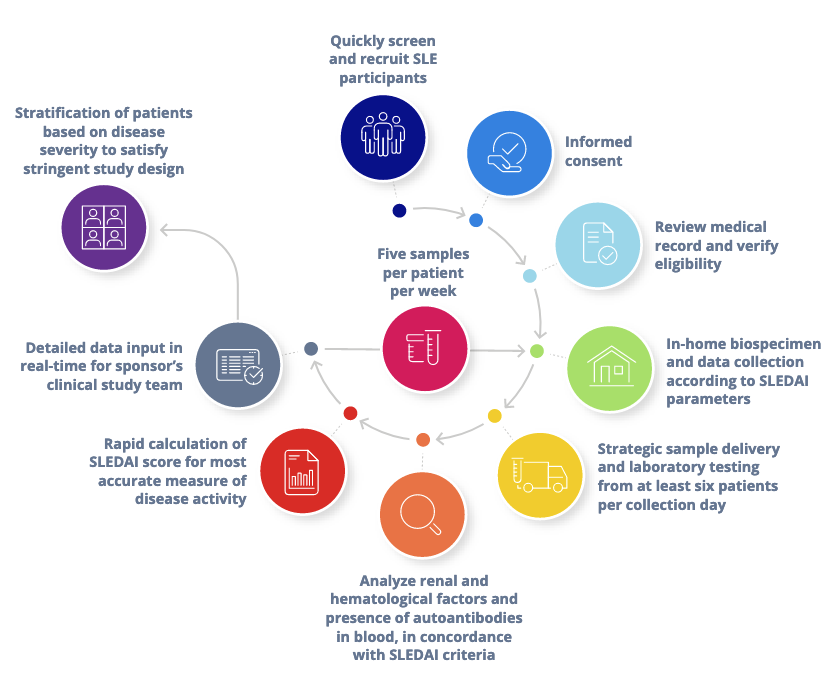
Taking a direct-to-patient approach for accurate assessment of
SLE disease activity using the SLEDAI.
We deployed our experienced team regularly to each enrolled participant’s home to assess the defined 24 clinical and laboratory variables required to make a SLEDAI score calculation. Maximizing efficiency at each step of the workflow, we built a participant pool of varying disease severity for the study sponsor, thereby enabling the accurate measurement and characterization of SLE disease activity.
REFERENCES
¹ Mikdashi J and Nived O. Measuring disease activity in adults with systemic lupus erythematosus: the challenges of administrative burden and
responsiveness to patient concerns in clinical research. Arthritis Res Ther, 2015;17(1):183.


